Thermal paste, pad and adhesive
Thermal conduction agents are elementary components of a cooling system, as they can significantly optimize heat transfer between the heat source (e.g. microchips) and a heat sink. Thermal conductive agents are not only used in the computer and server sector, but also in the cooling of industrial machines, motors, heating and cooling devices and, for example, 3D printers. Before you buy a thermal paste, thermal pad or even thermal adhesive, for example, weigh the required performance, properties, service life and also the ability to bridge gaps with your project.
A brief overview of thermal conductors:
| Paste | Pad | Adhesive | Liquid metal | Peltier gel | |
 |  |  |  |  | |
 |  |  |  |  | |
 |  |  |  |  | |
 |  |  |  |  | |
 |  |  |  |  | |
 |  |  |  |  |
 Low Low |  Medium Medium |  High High |
The thermal conductive materials differ depending on the area of application and requirements:
Thermal paste
Very good performance based on silicones and other fillers
In most cases, thermal pastes based on silicone oil or ceramic substrate in combination with metal oxides are used. In many cases, the thermal conductivity coefficient of these thermal pastes is in the range of 1 to 10 W/mK. Thanks to their pasty to viscous consistency, the application of heat-conducting paste is usually no problem - either manually or mechanically.
Due to their flexibility and ease of processing, regular thermal pastes can be used in all conceivable areas, as long as the requirements are not too high (for example, in terms of power dissipation).
Liquid metal thermal paste
Extremely high performance thanks to liquid metal
NIn addition to thermal pastes based on oils and subtrates, thermal pastes based on liquid metal can be used for particularly high requirements. Their thermal conductivity coefficient is usually in the range of 40 to 80 W/mK, which corresponds to a significant increase in performance. In the case of liquid metal thermal conduction pastes, however, care must be taken to ensure that (at least in the form of the pastes) there is no direct contact with aluminum. If the use of aluminum cannot be avoided, it is also possible to use liquid metal in the form of solid thermal conductive pads (Coollaboratory Liquid MetalPad). These require a so-called burn-in (reaching the melting temperature for a short time) for their full performance to unfold, so that the metal, which is then liquid for a short time, can fill all the unevenness.
Liquid metal thermal pastes and pads are used primarily for very high power dissipation in the computer, server and industrial sectors to provide the best possible support for heat transfer. More information on cooling with liquid metal thermal conductors can be found here: Liquid metal for cooling components
Buy liquid metal thermal paste now!
Thermal pad
Good performance and extremely easy to use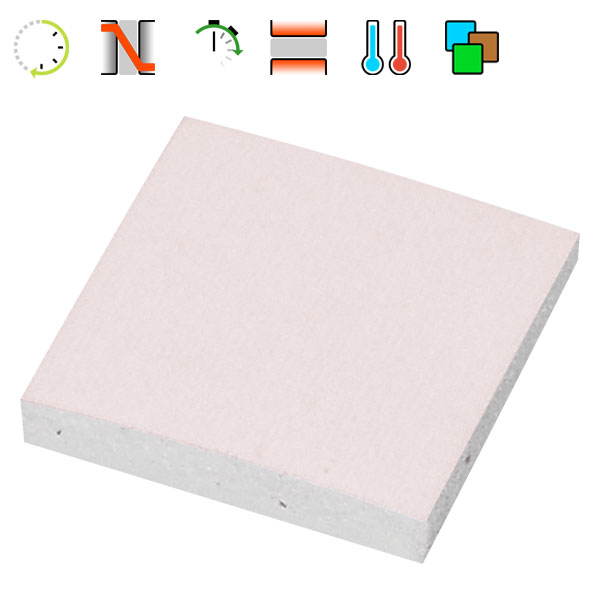
Similar to regular thermal pastes, most thermal pads are designed for lower power dissipation, but offer unparalleled ease of use, as the pads, which are often offered in a variety of thicknesses, are simply placed between the heat source and heat sink, and are also gap-filling. Thermal pads typically offer a slightly lower coefficient of thermal conductivity. Removing thermal pads is also usually very easy.
The heat conduction pad is used in a variety of applications, including wherever larger gaps between the heat source and cooler have to be bridged. In addition, its use can be observed above all in mass production due to its low cost as well as its extremely simple application.
Thermal adhesive
Good performance with a secure hold
In many areas, it is often the case that heat sinks cannot be securely fixed to the heat sources mechanically with screws or similar. In such a case, the use of a high quality and efficient thermal adhesive is the optimal solution to ensure the best possible dissipation of power loss to the heat sink.
Thermally conductive adhesives are two-component adhesives based on epoxies or silicones. Our High Silver Thermal adhesive also contains metallic fillers (silver) for optimum thermal conductivity. Thermal conductive adhesives usually have a processing time (pot life) of a few minutes up to one hour. This time indicates by when the adhesive applied between the heat sink and the heat source has cured.
To ensure optimum quality, we offer our High Silver Thermal adhesive in our online store. This is perfectly suitable for private as well as industrial purposes.
Peltier gel
High performance in conjunction with Peltier elements
When using a Peltier cooling system, it is not possible to use conventional thermal conductive pastes, as these usually consist of a carrier substance and fillers. When used with a Peltier cooling system, the carrier substance migrates away from the contact zone via capillary effects and cooling and heating cycles, with the result that the dry filler would remain between the Peltier element and the cooler (heat exchanger). The result is insufficient dissipation of waste heat from the Peltier element to the heat sink and damage or destruction of the Peltier element.
Similar to thermal conductive adhesives, Peltier gel also consists of two components, which are usually mixed 1:1 for the application. However, the gel remains viscous, which means that the heat exchanger can be detached from the Peltier element by hand at any time.
